The problem of burns are :
- Hundreds of person get burnt everyday
- A number of them die every day
- Treatment of burns in hospital is very costly – beyond the reach of a common man
- Even of the victim’s life is saved, disfigurement or crippling disabilities follow in most cases making their life miserable
- Preventing burns is simple and always better than cure.
Simple ways of preventing burns are :
- Don’t allow children to play in the kitchen.
- Cook on a raised platform.
- Don’t over pump the stove.
- Don’t pour kerosene when the stove is lit.
- Wipe dry kerosene split on the floor and then light the stove
- Don’t store the cooking material above the platform. Storage underneath the platform will reduce the risk of clothes catching fire.
- Turn off the cylinder valve and burner knob of the gas stove after cooking.
- In case of Burn, POUR WATER immediately.
- If your clothes are on fire, POUR WATER ON BURNS TILL THE BURNING SENSATION SUBSIDES.
- Don’t pull off the clothes sticking over the burn area.
- Don’t apply any ointment without medical advice.
- Cover with a clean sheet and refer to a doctor immediately.
- Water douses flame and controls fire quickly. It cools the sking and stops further damage to skin. It is mostly available in kitchen where mostly burns occur.
- Presence of blisters is a good sign indicating that your skin is alive. Such wounds heal fast. Dead skin does not form blisters. Don’t disturb blisters. Go to a doctor.
- Blanket traps the heat within and it continues its damaging action even on the deeper layer of the skin and as a result more damage & severer the damges, lesser the chances of survival.
- “Prevention is better than cure”. Form the habit to handle fire safely, be safety conscious, prevent burns and in case anyone is burnt, remeber to pour water on the burn surface immediately. Water is the best first aid in Burns.
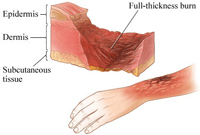
In burns, first the outermost layer is burnt and then the deeper layers. The depth of burns depends on the degree of heat and the time for which the skin was exposed to the heat. It is often seen that when the hand is burnt, the skin on the dorsum, being thinner, may be burnt fully, whereas on the palmer side the skin is thicker and not all of it gets burnt, cannot heal without a skin graft operation. Skin that is partly burnt, but still has some hair follicles, sweat glands and sebaceous glands will heal spontaneously in due course of time.

In case of a minor burn, hold the burnt part under the running tap water till the burning pain stops. Take the patient to his family physician who will advise treatment. Don’t remove clothing from the patients body. Pour water on the burnt area. Application of ice to the burnt area is soothing. Don’t apply ghee, oil or ointment. Continue First Aid during transport. Don’t give anything to eat until the doctor has seen him/her. Give water to drink.
- Skin is needed in major burns and other injuries where it helps to prevent infections, decreases pain and provides mechanical protection and thus helps faster healing and save life.
- Age above 18 years, not having transmissible diseases like hepatitis or HIV, skin cancer or skin diseases.
- No inner organs are exposed. No Bleeding from the area of skin donation.
- Will my decision to become skin donor affect the quality of my medical care?
- No. Organ and tissue recovery happens only after every effort has been made to save your life, and death has been legally declared.
- A system is in place to use skin donation fairly. Factors such as race, gender, age, income and celebrity and NOT considered when determining who receives skin donations. Furthermore, the buying and selling of organs, tissues and eyes is illegal.
 Donated skin can be used as a temporary covering for severely burned patients awaiting grafting procedures. The donated skin functions as the burned patient’s own skin for a short time, reducing pain and decreasing the risk of infection. In many cases, the availability of donated skin can help save the lives of burned patients.
Donated skin can be used as a temporary covering for severely burned patients awaiting grafting procedures. The donated skin functions as the burned patient’s own skin for a short time, reducing pain and decreasing the risk of infection. In many cases, the availability of donated skin can help save the lives of burned patients.
Advances in medicine and tissue preservation now make it possible to use skin in other procedures. In addition to use as a temporary skin covering, donated dermal grafts can now be used to replace lost dermis and can significantly reduce scarring, restore mobility and minimize the use of the patient’s own skin. Dermal grafts are also used to fill soft tissue defects as a result of cancer or trauma, to restore bladder control in the treatment of incontinence, in periodontal surgery to correct gingival defects and to facilitate abdominal wall repair for hernias or other injuries.
- Skin is obtained by a surgical procedure. Skin grafts are typically recovered from the back, abdomen and legs and may vary in thickness from .005” to .035”. In most instances, the procedure takes one to two hours.
- There are more than an estimated 90,000 people currently waiting for a life-saving organ transplant.
- Donated skin is prepared for transplantation in one of two ways. The tissue can be prepared by traditional methods of cell preservation which include maintaining cell viability via tissue culture techniques or cryopreservation. More recently, donated skin grafts can be preserved by utilizing advanced technologies to remove the cellular components of the grafts while maintaining the biochemical and structural characteristics. As a result, these donated skin grafts can be transplanted successfully without rejection. This technology greatly expands the clinical applications of donated skin.
- You can get more information regarding skin donation from National Burns Centre, Airoli. You can either email them on indianburnsrs@vsnl.net or can call them up on +91-22-27606660 / 61 / 62 / 63 /64.
